December 2, 2024
What is Bicipital Tendinitis: Understanding the Pain
- Short head tendon: Attaches to the coracoid process, a bony projection on the shoulder blade.
- Long head tendon: Runs through the bicipital groove, a channel in the shoulder joint
When these tendons become inflamed or irritated, it can cause significant pain and discomfort, particularly during activities that involve shoulder movement. Biceps tendinitis doesn’t typically occur alone. It most often happens alongside other shoulder issues, like Shoulder arthritis, Dislocated shoulder or Shoulder impingement syndrome.
What Causes Bicipital Tendinitis?
A variety of factors can contribute to the development of bicipital tendinitis, including:
- Repetitive overhead motions: Activities that involve lifting the arms above shoulder level, such as swimming, tennis, painting, or weightlifting, can put repeated stress on the bicep’s tendons. This can lead to inflammation and irritation, especially if the activities are performed with improper form or excessive force.

- Poor Posture: Slouching or hunching can put excessive stress on the shoulder joint and the biceps tendons.
- Injury: A sudden injury, such as a fall or direct blow to the shoulder, can damage the tendons.
- Age-Related Wear and Tear: As we age, the tendons in our bodies can become weaker and more susceptible to injury.
- Underlying Conditions: Conditions like shoulder instability or rotator cuff tears can increase the risk of bicipital tendinitis.
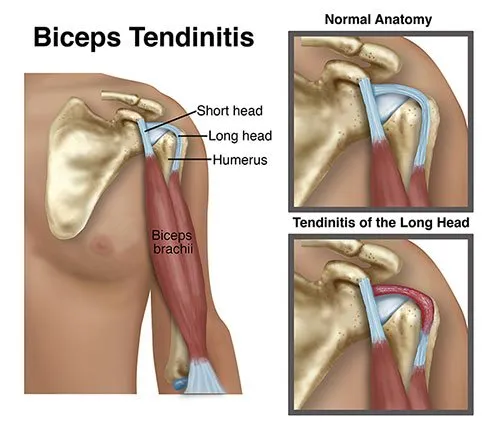
Symptoms of Bicipital Tendinitis
The primary symptoms of bicipital tendinitis include:
- Pain: Sharp or dull pain in the front portion of the shoulder, which may radiate down the upper arm.
- Tenderness: Tenderness to touch in the front portion of the shoulder, particularly around the biceps tendon.
- Weakness: Difficulty in lifting objects or performing overhead activities.
- Crepitus: A crackling or popping sensation while moving the shoulder.
- Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty in rotating the shoulder or lifting the arm overhead.
Diagnosis of Bicipital Tendinitis
To diagnose bicipital tendinitis, a healthcare professional will typically conduct a physical examination which involves checking the shoulder on parameters like range of motion, strength and signs of instability. Other than that they may also ask for imaging tests, such as:
- X-rays: To rule out other conditions, such as bone spurs or arthritis.
- MRI: To visualize the soft tissues, including the tendons, and assess the extent of damage.
- Ultrasound: To assess tendon inflammation and potential tears.
Treatment for Bicipital Tendinitis
The treatment for bicipital tendinitis, typically starts with noninvasive (nonsurgical) methods like:
- Ice: Applying ice packs to the shoulder for 15-20 minutes, several times a day.
- Rest:Avoiding activities that aggravate the condition.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter pain relievers belonging to NSAIDs can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physiotherapy: A physiotherapist can teach you specific exercises to strengthen the shoulder muscles and improve flexibility.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In severe cases, a corticosteroid injection can help reduce inflammation quickly.
- Bracing: Wearing a shoulder brace can help support the shoulder joint and reduce stress on the tendon.

- Ultrasound therapy: Ultrasound therapy can help reduce pain and inflammation by increasing blood flow to the injured area.
- Electrical stimulation: Electrical stimulation can help reduce pain and inflammation by blocking pain signals and stimulating muscle contractions.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and Stem cell therapy: PRP therapy and stem cells therapy involves injecting concentrated platelets and stem cells into the injured tendon to promote healing.
If noninvasive methods don’t help improve your condition, surgeon may suggest surgery. The doctor will most likely perform the surgery arthroscopically- inserting a small camera (arthroscope) in your shoulder joint to take pictures, which will help them guide the procedure using small surgical instruments. Surgical options may include:
- Biceps tenodesis: surgeon will remove the damaged section of your bicep and reattach the remaining tendon to your upper arm bone (humerus).
- Tenotomy: surgeon will release your damaged biceps tendon from its attachment.
Preventing Bicipital Tendinitis
To prevent bicipital tendinitis, consider the following tips:
- Proper Form: Use proper form and technique when performing any physical activity, especially those that involve overhead motions.
- Gradual Progression: Gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts to avoid overtraining.
- Strength Training: Incorporate strength training exercises to strengthen the shoulder muscles.
- Rest and Recovery: Allow adequate rest and recovery time between workouts.
- Ergonomic Considerations: Ensure your workspace is ergonomically designed to minimize strain on your shoulders.
- Stretching: Regular stretching can help improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension.
To conclude, Bicipital tendinitis is a common and painful condition that can affect people of all ages. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take steps to manage your condition and prevent future problems. If you are experiencing shoulder pain, it is important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Always consult a doctor
How can ORONAC GEL help?
For almost four decades now, ORONAC GEL has been helping individuals cure knee pain and other body pain ailments, such as joint pain, neck pain, and ankle pain. ORONAC GEL contain Diclofenac (No.1 Doctor’s prescribed active) that provides instant and long-lasting relief from knee pains and helps you get back on your feet in no time ORONAC GEL is a non-sticky, fast-absorbing product that directly targets the source of the pain, creates a warming sensation, and provides long-lasting relief from pain.

