November 2, 2024
Who Does Whiplash Affect?
Whiplash can affect anyone at any age, but is more likely to cause serious or lasting injuries in older adults and women and people assigned female at birth (AFAB). Older adults ( over age 65) are more prone to muscle and bone injuries due to age-related deterioration and weakening. These two groups are more likely to have whiplash-type injuries in car crashes due to several factors:
- Height: Experts suspect that’s because women and people AFAB have a shorter average height compared to men and people assigned male at birth (AMAB).
- Spine structure differences: Women and people AFAB also have a different spinal column structure than men and people AMAB. That affects the distance between each vertebra (the interlocking bones that make up your spine).
- Muscle differences: These groups usually have less muscle tissue, which can act as a shock absorber to reduce the effects of sudden impact forces. That means they have less available muscle to help absorb movement forces.
- Vehicle Construction: Modern vehicle construction may increase the risk of injury for women and those with AFAB due to the use of headrests in collisions. The height of seat back and headrests may affect these individuals differently due to their shorter average height.
Symptoms of Whiplash
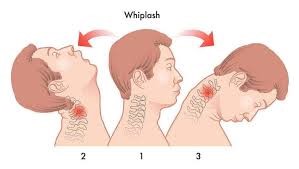
Symptoms can begin immediately after a crash or take at least 12 hours to appear depending on the severity of the injury and the extent of neck hyperextension or compression.
The Quebec Classification of Whiplash-Associated Disorders is a grading system created by experts to assess the severity of whiplash-associated disorders. the Grading system is as follows:
- Grade 1: The patient reports neck pain, stiffness, or tenderness without any positive physical exam results.
- Grade 2: Symptoms include pain affecting nearby areas like the head, face, shoulder, and back, muscle spasms making movement difficult, and physical signs of injury such as bruising, swelling, and sensitivity to touch.
- Grade 3: neurological condition characterized by muscle weakness, numbness, paraesthesia, headaches, vision problems, hoarseness or loss of voice, difficulty in swallowing, and cervical vertigo. These symptoms occur due to swelling or inflammation disrupting nerve signals in the injured area, affecting the ability to feel hot, cold, or pain. They require immediate attention.
- Grade 4: involving severe neurological symptoms, often indicating a fracture or shift in a neck vertebra, putting pressure on the spinal cord or nearby nerves, and often involving all symptoms mentioned above.
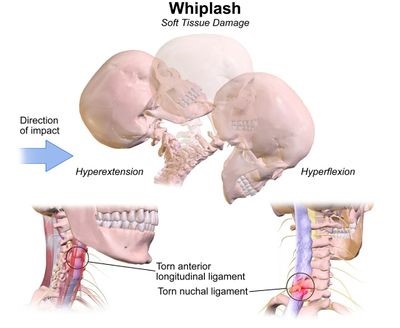
What Causes Whiplash
- Car accidents: Although rear-end crashes are the most prevalent cause of whiplash, it can occur in other types of car accidents.
- Sports injuries: Contact sports like football and hockey might increase the risk of whiplash.
- Falls: Falling from a height or sliding and falling can result in whiplash, particularly if the head hits a hard surface.
- Assaults: Violent shaking or being thrown to the ground can cause whiplash.
- Other incidents: Amusement park attractions, industrial accidents, and even rapid car brakes can all result in whiplash.
How is Whiplash diagnosed
In addition to a full health history and physical exam, testing for whiplash may include:
X-ray: Electromagnetic energy beams create pictures of inside tissues, bones, and organs on film. However, many whiplash injuries cause damage to soft tissue that cannot be detected on X-rays.
MRI: Large magnets and a computer create precise photographs of organs and soft tissue structures in your body.
CT scan: X-rays and computer technologies can provide detailed pictures of any region of your body, including bones, muscles, fat, and organs. CT scans are more detailed than regular X-rays.
Treatment for Whiplash:
Depending on the severity of the injury and the individual’s symptoms common treatment options include:
- Rest and ice: Resting the neck and using ice packs might help to relieve the pain and swelling.
- Over-the-counter pain treatments: include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) and topical gels.
- Physical therapy: will improve range of motion, strengthen neck muscles, and alleviate discomfort.
- Massage therapy: A gentle massage can help relax muscles and relieve stress.
- Chiropractic care: Some patients get relief from chiropractic adjustments.
- Prescription medications: In extreme circumstances, prescription pain relievers or muscle relaxants may be required.
Whiplash Prevention Measures:
- Wear seatbelts to protect head and neck in car accidents.
- Drive defensively to anticipate potential hazards.
- Wear appropriate safety gear, like helmets, during sports or activities involving whiplash.
- Maintain good posture to prevent neck and shoulder strain.
- Regular neck exercises to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility.
To conclude, Whiplash is a common injury that can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for whiplash, individuals can take steps to prevent and manage this condition.
Image Source: Cleveland Clinic
Always consult a doctor
How can ORONAC GEL help?
For almost four decades now, ORONAC GEL has been helping individuals cure knee pain and other body pain ailments, such as joint pain, neck pain, and ankle pain. ORONAC GEL contain Diclofenac (No.1 Doctor’s prescribed active) that provides instant and long-lasting relief from knee pains and helps you get back on your feet in no time ORONAC GEL is a non-sticky, fast-absorbing product that directly targets the source of the pain, creates a warming sensation, and provides long-lasting relief from pain.